
|
|
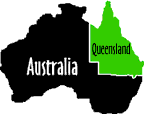 Humans HumansSkin Cancer The relation between skin cancer and uv radiation is well established. People of fair skin are generally more prone to skin cancer. For example, Queensland, Australia, which has high natural rates of uv radiation and a population largely of Northern European descent, has the highest rate of skin cancer in the world.
Damage to DNA is responsible for skin cancer. Except for a variety called melanoma, skin cancer is usually easily treatable. Although the relation between uv radiation and the other types of skin cancer is well understood, its connection with melanoma is not. However, we know that melanoma rates are twice as high in southern states such asTexas and Florida as they are in northern states such as Wisconsin and Montana.
But, even with the large percentage increase of uv radiation at high latitudes in the Southern Hemisphere, the rates there are still considerably less than rates at lower latitudes. Even though the greatest destruction of ozone occurs in the vicinity of Antarctica, it is clear that the amount of uv radiation reaching the surface at Ushaia (55S) during spring and summer is comparable to that reaching the ground in the vicinity of Buenos Aires (34S). However, because organisms at these high latitudes have adapted to only low levels of uv radiation, the large percentage increase of this radiation is potentially very dangerous. Cataracts and Other Eye Disorders Cataracts are a clouding of the lens of the eye that, if untreated, can lead to blindness. Although cataracts are easily treatable, this treatment may not be available to many people in developing countries. Consequently, UNEP estimates that a 1% decrease in ozone concentrations will cause 100,000 additional people to go blind. Although blindness is a real threat from reduced ozone, sometimes news stories can contain exaggerations. For example, pictures of sheep in South America with a caption that read "blinded by uv radiation" were actually pictures of sheep suffering from pinkeye, a common illness. Pterygia and pingueculae are other eye disorders that may be related to uv radiation exposure. A pterygium is a growth that begins in the corner of the eye and grows toward the cornea. Pterygia rarely cause major problems, but, if left untreated, may result in blindness. A pinguecala, which occasionally develops into a pterygium, is a yellow patch that forms on the white part of the eye. Human Immune System Some researchers believe they have found a link between increased uvb radiation and reduced effectiveness of the human immune system, which leads to reduced effectiveness of inoculations as well as increased susceptibility to infections. [ Humans ] [
Animal Life ] [ Plant Life ] [ Home ] [ Teacher Pages ] [ Modules & Activities ] |
HTML code by Chris Kreger
Maintained by ETE Team
Last updated April 28, 2005
Some images © 2004 www.clipart.com
Privacy Statement and Copyright © 1997-2004 by Wheeling Jesuit University/NASA-supported Classroom of the Future. All rights reserved.
Center for Educational Technologies, Circuit Board/Apple graphic logo, and COTF Classroom of the Future logo are registered trademarks of Wheeling Jesuit University.